This quick start guide will walk you through the basics of using JSON Web Tokens (JWT) in a Mattermost App in Go. In this guide you will review an App that:
manifest.json, declares itself an HTTP application that uses a bot account, uses JWT, and attaches UI elements to locations in the Mattermost interface.send function to a /hello-jwt command and wraps it with a function to authenticate JWT.Why you would want to use JWT for App development? Using a token, your App can validate the legitimacy of any request by ensuring it’s coming from the expected Mattermost server. Simply put, implementing JWT will enhance your App’s security and functionality via a handshake.
Before you can start with your App, you should first set up your environment by following the developer setup guide.
You also need Go v1.16 or later installed. Please follow the official guide to install the latest version.
In the same mattermost-app-examples repository you cloned via the developer setup guide above, navigate to the `golang/jwt` directory and start the Docker container:
cd golang/jwt
docker compose up
You’ll see Docker install the Go modules and then the App will come online and print the following message:
Use '/apps install http http://mattermost-apps-golang-jwt:8084/manifest.json' to install the app
Use "1234" as the app's JWT secret
The secret comes from this line in hello.go:
var secret = []byte("1234")
In a production app, you should generate the secret at random per App installation, and store on the App’s end to identify the specific Mattermost server.
Next, access your development Mattermost Server at http://localhost:8065 and use the /apps install http http://mattermost-apps-golang-jwt:8084/manifest.json slash command to install the JWT App. Select Agree to grant the app access to APIs and Locations, enter the JWT secret (1234), and click Submit to finish the installation.
You can now use the /hello-jwt send command. This will cause the App’s bot user to direct message (DM) you a response:
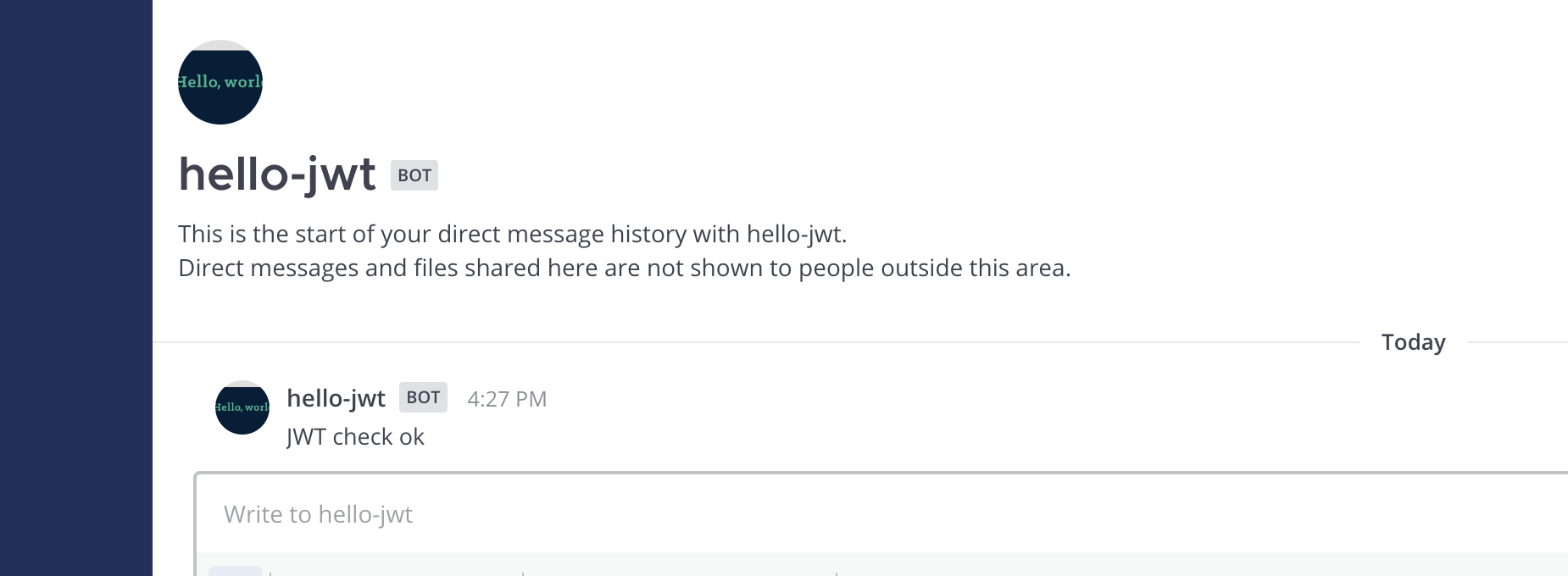
To understand the App, examine the following elements:
The App must provide a manifest, which declares App metadata. In this example, the following permissions are requested via the /manifest.json endpoint:
Bindings specify how an App’s calls should be displayed and invoked from these locations. Locations are named elements in the Mattermost user interface.
The App creates a /hello-jwt send slash command that checks the validity of the JWT.
Call handlers are functions that respond to user interactions and webhook events. The JWT App relies on one main call handler:
send that services the command and modal form submissions. This function is wrapped with withJWT that requires JWT, which calls checkJWT to verify the provided token.Apps may include static assets. Only one asset is used in this example for this App: icon.png. Static assets must be served under the static path.
Once you’re done with the App, you can uninstall it via the /apps uninstall hello-jwt slash command. Alternatively, you can use /apps debug clean to remove all data for all installed Apps.
To stop and clean up the App from Docker after you’re done, use the following command in the golang/jwt directory:
docker compose down
You now know how to create a Mattermost App in Go that uses JWTs. If you have questions about building Apps or want to show off what you’re building, join us on the Mattermost Apps channel in the Mattermost Community server!