There are several renderer processes that make up the internal interface of the Desktop App. These are all represented by singleton objects that reside in the Main Module. These classes are in charge of holding the corresponding BrowserWindow or BrowserView object, initializing any handlers specific to that view, and exposing any special functionality that other modules may need to either read or affect the view.
As all of these views only load trusted scripts in the renderer process, all of these views are given full access to the desktopAPI module, allowing them to perform basically any action that we allow for in the Desktop App via the IPC layer.
These are the internally-managed windows acting as the main user interface points for the user. Each of these views are represented by a BrowserWindow object.
This is the primary view that encapsulates the core of the Desktop App interface. Most BrowserView objects are rendered using this window as their parent, and are affected by the behavior of this window. Most other controls, including the tray icon and taskbar/dock icon, interact with this window, and most of their functionality is tied to it as well.
This window is managed by the MainWindow module located at main/windows/mainWindow.
init(): Creates the BrowserWindow object for the Main Window and adds all appropriate listeners.get(): Returns the BrowserWindow object for the Main Window. This is directly exposed as there are many different functions affecting the behavior of the window, and thus the encapsulating module often needs to pass that control to other modules. If true is passed as an argument, init() will be called if the window does not exist, otherwise undefined is returned.getBounds(): Returns the current size and location of the BrowserWindow, used for resize functionality, and to ensure that child windows/views are positioned correctly.focusThreeDotMenu(): Sends a message to the Main process that focuses the view and highlights and focuses the 3-dot menu on Windows/Linux. This is used when the ALT key is pressed as a shortcut to focus the menu.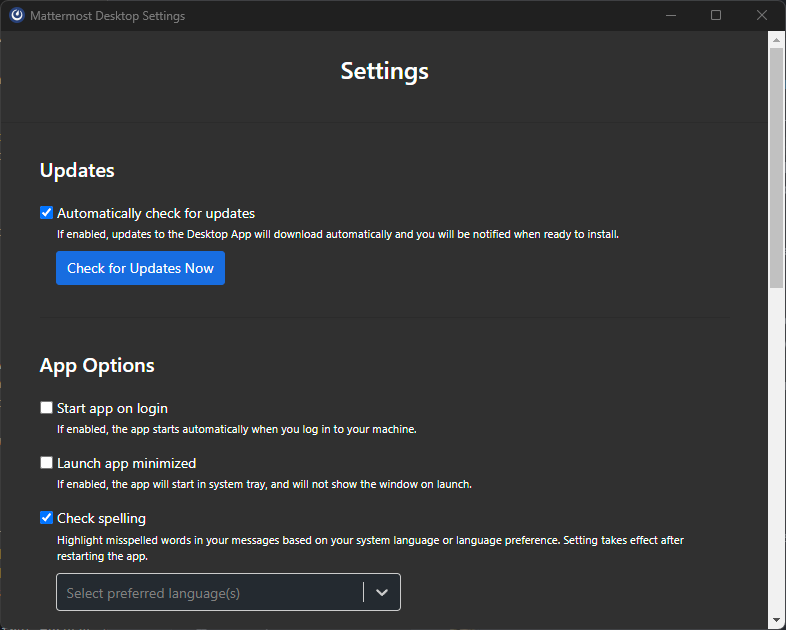
This window is created when the user opens Preferences from the File menu. It contains an interface where the user can change settings specific to the Desktop App client that do not affect their Mattermost servers. This window is a child window of the Main Window and will close/hide when the Main Window is closed/hidden.
This window is managed by the SettingsWindow module located at main/windows/settingsWindow.
show(): Shows the Settings Window if it exists and will create it if does not. When the window is closed, the BrowserWindow object is dereferenced.get(): Retrieves the Settings Window BrowserWindow object if it exists and returns undefined if it does not.These are the internally managed views that are rendered on top of existing windows, adding additional functionality. Each of these views are represented by a BrowserView object.
Most of these views exist as they act as augments to the existing interface and must be rendered over top of the external sandbox Mattermost BrowserViews.

This is a BrowserView that renders over top of external Mattermost views that are loading. It is a cosmetic view that avoids the user having a white screen while the application is loading. The view is ephemeral should only be visible while the current external Mattermost view is loading.
This view is managed by the LoadingScreen module located at main/views/loadingScreen. Its parent is the Main Window.
show(): Displays the Loading Screen over top of any other BrowserView currently rendered in the Main Window and begins the animation.fade(): Starts the process of removing the Loading Screen. First a signal is sent to the renderer to fade the screen and stop the animation. When that finishes, the view is removed from the window.setBounds(): Calls when the Main Window resizes while the Loading Screen is still visible and the view needs to change its size as well.setDarkMode(): Calls when the application’s dark mode flag is changed, to ensure a consistent color scheme.isHidden(): Helper method to check whether the view is hidden or not.